The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), sometimes called the EITC, is a kind of tax credit called the EIC, which is a tax credit earned on low- and moderate-income workers.
Eligibility for tax credits depends on many factors, including family size, tax records and income. When the EITC exceeds the tax owed, tax refunds will be issued to those who claim and qualify for the credit. The loan will be limited to income.
How does the Earned Income Tax Credit work?
The Earned Income Tax credit is refundable. Because it is refundable, the beneficiary does not need to pay taxes to procure the benefit. The earned income tax credit comes under section 32 of the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) and is a part of the federal income tax system.
The IRS data reports over 26 million beneficiaries for the earned income tax credit. The year 2020 saw these taxpayers receive $59 billion from the EITC. This made the earned income tax credit the largest anti-poverty scheme providing cash benefits to the people.
Recipient’s earned income is calculated using one of the 8 different formulas. The calculation however depends on several factors and in addition to that the number of children the taxpayer has and whether he/she is married or not. The credit is more if the taxpayer has more children.
Who is eligible for earned income tax credit?
Following is the list that provides for the eligibility criteria to claim EITC:
- The recipient must earn an income.
- He/she must file a federal income tax return.
- Certain residency requirements must be fulfilled by the taxpayer.
- A taxpayer’s children must meet social, residence, and age requirements to be considered a credit-eligible child.
- There is a certain limit for investment income. A taxpayer’s income must fall under that maximum limit.
- Childless workers must be between the ages of 25 and 64 to claim the credit. However, this age requirement does not apply to EITC claimants with qualifying children.
- Taxpayers are required to provide Social Security Numbers (SSNs) for themselves, their spouse (if married), and their children claiming the credit.
- A taxpayer cannot be denied the credit due to fraud or neglect of the rules when claiming the EITC.
* A taxpayer with an income more than the mentioned limit will automatically considered ineligible.
* A taxpayer who does not have an eligible child but can claim as a dependent on another person's tax return is not eligible for the EITC. Additionally, applicants who are ineligible minors must have lived in the United States for more than six months.
*The SSN must be issued either to a citizen of the United States or in accordance to the provision of the Social Security Act relating to the lawful admission for employment in the United States.
How to claim Earned Income Tax Credit
By now if you know that you qualify for the earned Income Tax Credit you must beware of the fact that the IRS issues the earned income tax credit after mid-February. If you find yourself eligible for the earned income tax credit, you have to wait for about three years from the due date of you’re return to claim the refund.
EITC and other funds such as ACTC (Additional Child Tax Credit) usually face delays. There is an app named IRS2Go which helps you track your refund. However, the taxpayer receives the refund by the 1st of March in case of no discrepancies.
While applying make sure you use the correct forms, Form 1040 or Form 1040 SR. If you are claiming with a qualifying child, mention the schedule EIC. Use Form 1040 and Schedule EIC (if applicable) to file a prior year, or you can file a new form if you previously filed a tax return but did not claim the EITC when you were eligible.
How much do I earn From EITC?
The earned income includes:
- Wages on which federal income taxes are withheld.
- Income earned where your employer did not refuse tax.
- Self-employed money.
- Benefits earned from a union strike.
- Non-taxable combat pay. This earned income either increases or decreases your EITC.
What an earned income does not include:
1. Pay you got for work when you were an inmate in a penal institution.
2. Interest and dividends.
3. Pensions or annuities
4. Social Security
5. Unemployment benefits
6. Alimony
7. Child supportEarned income Tax Credit table
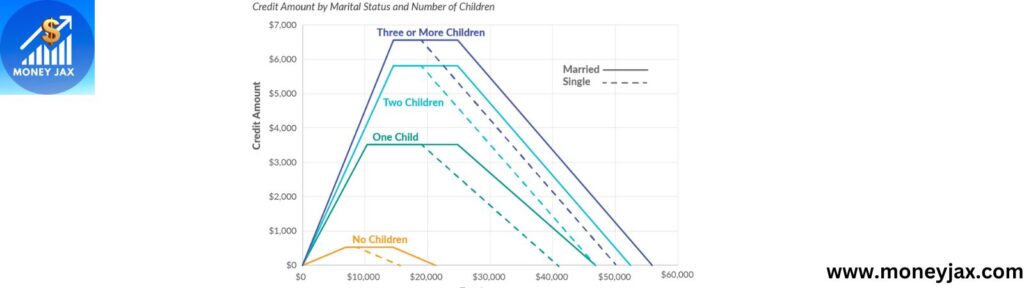
How has Earned income tax Credit benefited people
Reduction of Poverty
The census carried out in the year 2018 gives an account that the EITC lifted about 5.6 million people above the poverty line. These people also included nearly 3 million children, based on the Supplemental Poverty Measure (SPM).
The earned income tax credit decreased one-fourth of the children from falling below the poverty line. The credit reduced the severity of poverty for 16.5 million people, including about 6 million children, based on the SPM.
Earned income tax credit along with the child tax credit was responsible for the upliftment of 10.6 million people above the SPM poverty line and made poverty less severe for 17.5 million others in 2018.
Credit Growth
Working families are eligible for the EITC based on their income. The EITC for families earning low income increases on increase with the income until the credit is maximum.
How frequently the EITC changes depends on marital status and the number of children. Consider an example, a couple with 2 children would have a level-in rate of 40% which means their EITC would increase each time their income reached a certain level. An additional 40 cents is given for each dollar. On the other hand, for high-income families, the EITC is phased out from the set amount until it reaches zero.
Fixed the Meager EITC for Workers not having children
EITC for workers without children was expanded under the American Rescue Plan Act for the tax year 2021, by raising the maximum from roughly $540 to roughly $1,500 and raising the income cap for these adults to qualify from about $16,000 to at least $21,000.
Younger adults falling in the range19-24 were also considered eligible under working adults without children. People aged 65 and above were also included.
This proved to be beneficial for about 17 million people. It provided support to people who worked for low pay. However, the expansion of EITC under the American Rescue Plan Act was effective for the tax year 2021 only.
Consequences of an error related to the Earned Income Tax Credit
Certain errors in your tax form could not just only delay the refund for some days but for several months. Not only this, but it could also result in the denial of the earned income tax credit by the IRS.
If your whole claim is denied by the IRS:
- You must repay the EIC amount paid in error with interest.
- To re-apply for EIC you may need to submit form 8862 titled ” Information To Claim Certain Credits After Disallowance.”
- If the IRS finds that you filed a tax return due to “reckless or intentional disregard of the rules.” you will be barred from claiming the EITC for the next two years.
- If the IRS determines that you filed your tax return fraudulently, you may be barred from claiming the EITC for the next 10 years.
Free Resources to help you file your tax return
- EITC Brochure in Spanish/English
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
- Franchise Tax Board (FTB)
- CalEITC
Conclusion
If you didn’t claim the Earned Income Tax Credit when you filed for the same for the last 3 years but you think you qualify for it, the IRS requires amending to get a refund. The EITC is designed such that it provides financial assistance to low- and moderate-income workers and families.
It reduces the amount of taxes owed and provides refunds to eligible taxpayers. The amount of the credit depends on income, tax information, and eligible children.
For a piece of more information:
https://moneyjax.com/tax-and-investment-2024-new-year-new-goals/
Frequently Asked Questions
How worth it is the Earned Income Tax Credit?
Taking the time to discover about the Earned Income Credit and its eligibility criteria can pay off. The earned income tax credit benefits can be worth up to $7,430 as of 2023 depending on your filing status, income, and number of qualifying children.
What are the Earned Income Tax Credit income limits?
The most important parameter for figuring out who qualifies for the EITC is income level. So, if your income is higher than the limits, you can’t claim the credit. For the entire table visit: https://www.eitc.irs.gov/eitc-central/income-limits-and-range-of-eitc
How do I know if I qualify for an earned Incom Tax Credit?
There are some basic as well as special qualifying rules specified by the IRS. You must visit: https://www.irs.gov/credits-deductions/individuals/earned-income-tax-credit/who-qualifies-for-the-earned-income-tax-credit-eitc
What are some common errors in claiming the EITC/EIC?
Claiming a child who does not meet the qualifying tests for age.
Relationship and residency.
Social Security number or last name mismatches.
Filling as single or head of household when married.
Over or under-reporting of income or expenses.
Entering the incorrect amount of federal EITC/EIC credit.
What does it mean when you get a tax credit?
A tax credit is a dollar-for-dollar amount claimed by taxpayers on their tax return to reduce the income tax they owe.
